
Farming in the 21st century is rapidly changing. Climate change, urbanization, and increasing food demand are forcing agriculture to adopt innovative models. One of the most promising solutions is the vertical farming business. Unlike traditional farming, which depends on large plots of land and favorable weather, vertical farming grows crops in stacked layers using controlled environments.
For farmers and agripreneurs in the USA and Europe, this model opens a new window of opportunity. Urban demand and smart farming technologies are reshaping how we grow food in cities. With urban populations rising and demand for fresh, pesticide-free food increasing, starting a vertical farming business in 2025 can be both profitable and sustainable. But how exactly does it work, and what steps are needed to succeed? Let’s dive in.
What is Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming is a modern agricultural practice where crops are grown vertically in stacked systems, often inside buildings, shipping containers, or warehouses. These systems rely on indoor vertical farming techniques such as hydroponics, aeroponics, or aquaponics.
- Hydroponic vertical farming: Plants are grown in nutrient-rich water without soil.
- Aeroponic farming: Roots are suspended in the air and misted with nutrient solutions.
- Aquaponics: Combines hydroponics with fish farming, creating a closed-loop system.
Compared to traditional farming, vertical farming requires 90% less water, no pesticides, and much less land. Cities like New York, London, and Amsterdam are embracing urban vertical farming to meet local food demands.
Why Start a Vertical Farming Business in 2025?
Several factors make vertical farming attractive in 2025:
- Growing Food Demand → By 2050, the global population will reach nearly 10 billion, and urban centers in the USA and Europe will need localized food production (FAO Report).
- Sustainability Goals → Governments in the West are investing in climate-resilient farming solutions.
- Profit Opportunities → Fresh, pesticide-free greens can be sold at premium prices in urban markets, restaurants, and supermarkets.
- Space-Saving Agriculture → A vertical farm can produce up to 10 times more yield per square foot than traditional farms (USDA Research).
In short, vertical farming is not just a trend—it’s a business opportunity aligned with future food systems.
How Profitable is Vertical Farming?
One of the most common questions is: “Is vertical farming profitable?”
Yes, but profitability depends on scale, crop choice, and technology.
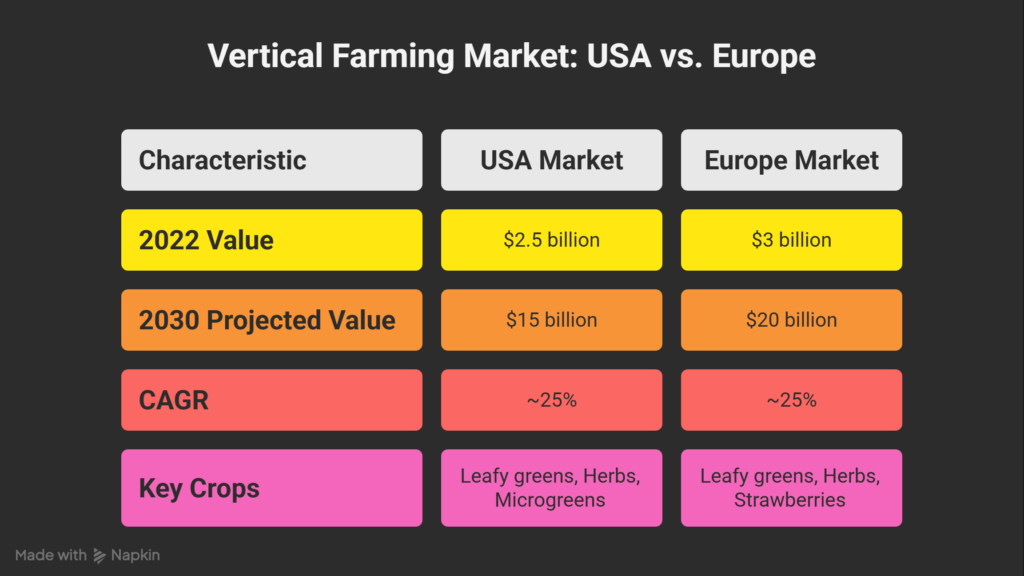
- According to Allied Market Research (2023), the global vertical farming market was valued at $5.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $35 billion by 2030.
- Leafy greens, herbs, strawberries, and microgreens offer the highest ROI because they grow fast and sell at premium prices.
- In the USA, small-scale vertical farms can achieve profit margins of 10–20% if managed efficiently.
The Agro Reality Newsletter
Get weekly insights on crops, livestock, sustainable practices, agricultural economics, and real-world farming challenges—delivered to your inbox.
Example ROI (Small-scale USA model):
| Crop Type | Yield (per sq. ft.) | Average Market Price | Profit Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lettuce | 20 heads/month | $1.50–$2/head | $30–$40 |
| Basil | 1 lb/month | $20–$25/lb | $20–$25 |
| Microgreens | 1–2 lbs/week | $20–$30/lb | $80–$120 |
Interesting Fact: A 10,000 sq. ft. vertical farm in New Jersey produces the same amount of lettuce as a 100-acre traditional farm.
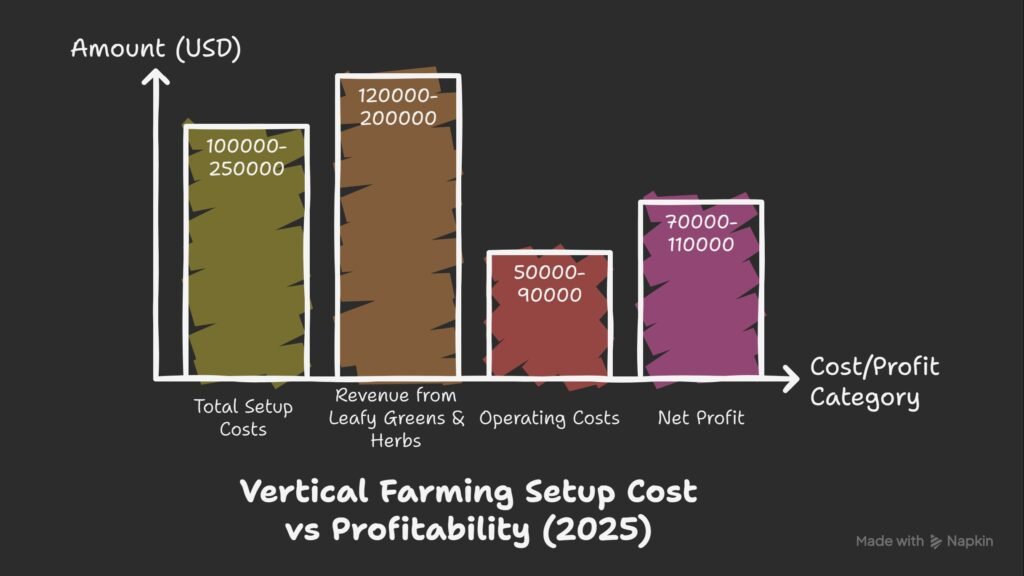
Cost of Vertical Farming Setup
Starting costs can be high, but so are the long-term returns.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (USA & Europe, 2025):
| Investment Item | Approximate Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Warehouse/Indoor Space | $50,000 – $200,000 |
| Hydroponic/Aeroponic System | $20,000 – $100,000 |
| LED Grow Lights | $15,000 – $50,000 |
| Climate Control & Sensors | $10,000 – $40,000 |
| Seeds, Nutrients, Supplies | $5,000 – $15,000 |
| Labor & Operations | $30,000 – $70,000 annually |
On average, setting up a small to medium-scale vertical farm costs $100,000–$250,000 in the USA or Europe.
While the initial investment is high, investors are attracted because vertical farms start generating returns within 2–3 years.
For a detailed startup budgeting template used in other indoor farms, check our Start a Profitable Mushroom Farming Business in 2025 post.
Vertical Farming Technology in 2025
The backbone of vertical farming is technology.
- Smart Sensors (IoT) → Monitor pH, humidity, and nutrients in real time.
- AI & Machine Learning → Optimize lighting, irrigation, and yield predictions.
- LED Lighting → Energy-efficient lights designed for plant growth.
- Automation & Robotics → Reduce labor cost and increase scalability.
These vertical farming technologies make the system efficient, but they also represent one of the largest expenses.
Vertical Farming USA vs Europe
- USA: Cities like New York, Chicago, and San Francisco are leading in commercial vertical farms. Companies like AeroFarms and Plenty have raised millions in investment.
- Europe: The Netherlands, Germany, and the UK are pioneers, with government support and tech-driven models. The EU’s Farm to Fork Strategy promotes sustainable practices like vertical farming.
Both markets are growing, but Europe emphasizes sustainability, while the USA focuses on scalability and profitability.
Investment Opportunities in Vertical Farming
Vertical farming attracts investors because of its high growth potential.
- In the USA, venture capitalists are funding startups like Bowery Farming and Plenty.
- In Europe, governments provide grants for vertical farming investment under sustainable agriculture programs.
- Crowdfunding platforms are also allowing small investors to join the movement.
According to PwC (2023), vertical farming is among the top five agri-tech investment areas in the West.
Step-by-Step Guide to Starting a Vertical Farming Business
Step 1: Market Research & Location
Choose an urban area where demand for fresh greens is high. Restaurants, hotels, and supermarkets are great target buyers.
Step 2: Choose the Right Technology
Decide between indoor vertical farming systems: hydroponics, aeroponics, or aquaponics.
Step 3: Calculate Costs & Secure Funding
Prepare a detailed business plan including startup cost of vertical farming. Explore grants, bank loans, or investor partnerships.
Step 4: Build a Skilled Team
Hire or train staff in hydroponics, plant science, and technology management.
Step 5: Crop Selection & Production
Start with high-demand crops like lettuce, basil, spinach, or strawberries.
Step 6: Marketing & Sales Strategy
Build relationships with local stores and restaurants. Highlight sustainability and freshness as your unique selling point.
Challenges & Risks in Vertical Farming
While the model is promising, it comes with challenges:
- High Energy Cost → LED lighting and climate control require significant electricity.
- Technology Dependence → Any system failure can cause large losses.
- Consumer Awareness → Some buyers are still unfamiliar with vertical farming products.
- Profitability Risks → Profit depends heavily on energy efficiency and crop choice.
Future of Vertical Farming (2025–2030)
- AI-driven fully automated farms
- Integration with renewable energy (solar, wind)
- Expansion into staple crops (wheat, rice)
- Wider adoption in climate-vulnerable regions
According to MarketsandMarkets (2023), vertical farming will grow at a CAGR of 25% between 2023 and 2030.
Conclusion
Vertical farming is more than just an innovation—it’s the future of sustainable agriculture. For agripreneurs in the USA and Europe, a vertical farming business in 2025 offers a chance to meet growing food demand, support environmental goals, and build profitable ventures.
Yes, the startup costs are significant, and challenges exist. But with the right technology, business model, and market strategy, vertical farming can deliver consistent profits and play a vital role in feeding future generations.
If you are ready to explore sustainable agribusiness, starting a vertical farming venture in 2025 might be the smartest move you can make.