
Garlic isn’t just a flavorful addition to food—it’s also a profitable crop for American farmers. With demand rising and a growing interest in local, organic food, garlic farming in the USA is becoming a smart choice for both beginner and experienced growers.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about starting a garlic farm in 2025—from choosing the right variety to estimating profits.
Why Garlic Farming USA is a Profitable Idea in 2025
In 2025, garlic remains one of the most consumed vegetables in the United States. Americans consume over 300 million pounds of garlic annually, and a large portion of that still comes from imports—especially China.
So, why grow garlic locally?
- Local garlic sells for up to 3x more than imported ones in farmer’s markets.
- Organic garlic is in high demand, especially in health-conscious communities.
- Garlic has a long shelf life and relatively low maintenance compared to other crops.
Bottom line: The USA needs more local garlic growers—and it could be you!
Best Garlic Varieties to Grow in the USA
There are two main types of garlic you can grow: hardneck and softneck.
Hardneck Garlic
- Best for cold climates (e.g., Northern USA)
- Strong flavor, easy to peel
- Examples: Rocambole, Purple Stripe, Porcelain
Softneck Garlic
- Best for warmer states (e.g., California, Texas)
- Longer shelf life, milder flavor
- Examples: Artichoke, Silverskin
Ideal Climate & Soil Conditions for Garlic Farming USA
Garlic grows well in most U.S. climates, but thrives under the right conditions.
Climate Needs
- Best planted in fall (Sept–Nov) for summer harvest
- Prefers cool temperatures during early growth
- Needs 6–8 hours of sunlight daily
Soil Requirements
- Loose, well-drained loamy soil
- pH between 6.0 and 7.0
- Organic matter-rich soil performs best
Top Garlic-Growing States
| State | Type | Special Note |
|---|---|---|
| California | Softneck | Largest garlic-producing state |
| Oregon | Hardneck | Ideal for organic farming |
| New York | Hardneck | Great for local markets |
| Texas | Softneck | Long growing season |
Step-by-Step Garlic Farming USA Process
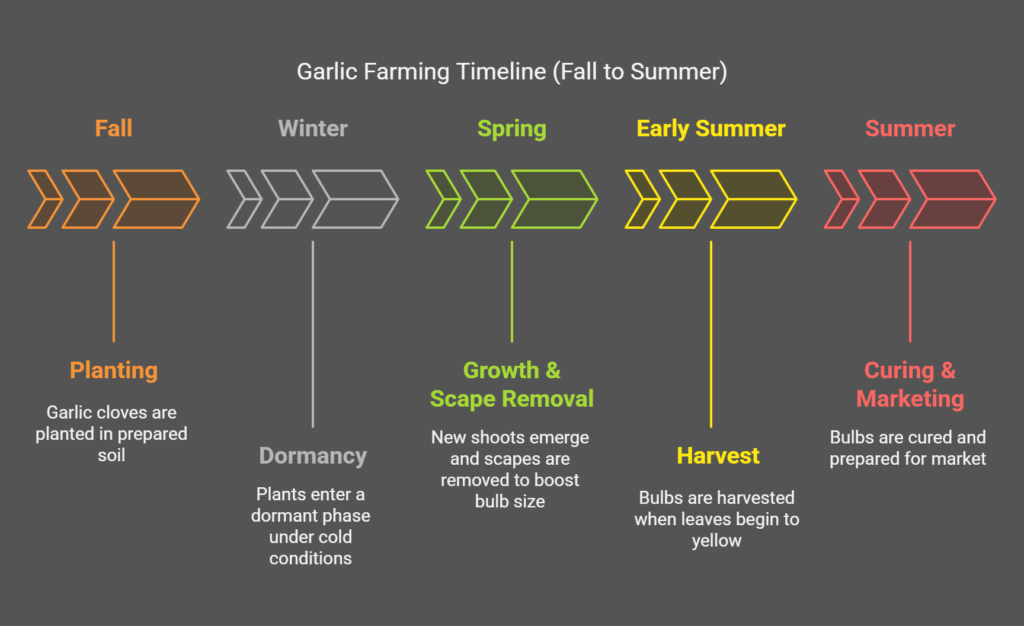
Here’s how you can get started:
1. Prepare the Land
- Till the soil 6–8 inches deep
- Remove weeds and mix compost or organic manure
2. Planting Garlic
- Use garlic cloves, not seeds
- Plant cloves 2 inches deep, 4–6 inches apart
- Keep rows 12–15 inches apart
3. Watering and Mulching
- Water weekly, especially during dry months
- Mulch with straw or leaves to retain moisture and suppress weeds
4. Pest & Disease Management in Garlic Farming USA
Even though garlic is naturally pest-resistant due to its strong aroma, certain pests and diseases can still affect yield—especially in humid or poorly managed farms. Successful garlic farming in the USA requires proactive and organic-friendly pest management strategies.
Common Diseases Affecting Garlic
| Disease Name | Symptoms | Organic Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| White Rot | Yellowing leaves, bulb decay | Use long-term crop rotation (4+ years), solarize soil before planting, and apply neem cake |
| Downy Mildew | Pale patches on leaves, stunted growth | Ensure proper spacing, improve airflow, and spray potassium bicarbonate |
| Basal Rot | Soft base of bulb, root rot | Avoid overwatering, improve drainage, and use disease-free seed cloves |
Common Pests
| Pest Name | Damage Caused | Natural Control Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Onion Thrips | Silver streaks on leaves, reduced growth | Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs, and spray neem oil |
| Aphids | Curling leaves, sticky residue | Use insecticidal soap or garlic-chili spray |
| Nematodes | Bulb deformation, plant stunting | Use hot water treatment for seed cloves and practice soil solarization |
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Tips:
- Rotate crops with non-allium vegetables to break disease cycles
- Apply compost tea or beneficial microbes to strengthen plant immunity
- Avoid planting garlic in the same soil where onions or leeks grew in the last 2 years
- Keep the field weed-free to reduce pest breeding grounds
Proactive pest management not only improves yield but also ensures your garlic meets USDA organic standards—an important selling point in the Western garlic farming USA market.
Harvesting and Curing Garlic

- Garlic is ready to harvest when 50% of leaves turn yellow-brown
- Loosen soil and gently pull out bulbs
- Dry under shade for 2–3 weeks with proper airflow
Storage Tip: Cured garlic can last 6–8 months in cool, dry conditions
Cost and Profit Estimation for Garlic Farming USA (Per Acre)
Here’s a simplified overview for 2025:
| Category | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Land Preparation | $300–$500 |
| Seed Cloves | $1,000–$1,500 |
| Fertilizer & Mulch | $250–$400 |
| Labor & Maintenance | $500–$700 |
| Harvesting & Curing | $300–$500 |
| Total Investment | $2,500–$3,500 |
Expected Yield per Acre: 10,000–15,000 lbs
Average Selling Price: $2–$4/lb (retail or organic market)
➡️ Potential Revenue: $20,000–$45,000
➡️ Estimated Profit: $15,000+ per acre (with proper planning)
Pro Tips for First-Time Garlic Farmers
- Start with 1/4 to 1 acre to learn the process
- Use local farmer networks or university extensions for region-specific advice
- Explore value-add options: garlic paste, powder, pickles
Interesting Fact
Did you know? Over 60% of garlic consumed in the USA is imported from China—yet local organic garlic often sells for more than triple the price!
Final Thoughts
Garlic farming in the USA is a low-risk, high-reward opportunity—especially in 2025 when local food demand is booming. Whether you’re a backyard grower or planning to scale commercially, garlic is a smart, sustainable crop to consider.
Recommended Read
“Top 10 Most Profitable Crops to Grow in Small Farms”
Coming Up Next:
Top 7 High-Demand Crops to Grow in Canada – Stay tuned!
🔗 Sources / References
- USDA National Agricultural Statistics Service – Garlic Crop Reports
👉 https://www.nass.usda.gov/
Provides updated statistics on garlic production, yield per acre, and state-wise crop data across the USA. - FAO – Garlic Market and Global Trade Data (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations)
👉 https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC
Detailed data on global garlic production, imports/exports, and price trends including figures relevant to the USA.
Pingback: How to Get Government Grants for Organic Farming in the USA - Agro Reality