Ecological Farming: A Sustainable Path for Western Agriculture

Introduction: What Is Ecological Farming and Why Does It Matter Today?
Ecological farming, often called agroecology, is a holistic approach to agriculture that works in harmony with nature to produce food sustainably. Unlike conventional farming, which often relies on synthetic chemicals and monocultures, or organic farming, which avoids synthetic inputs but may still prioritize large-scale production, it emphasizes biodiversity, soil health, and local ecosystems. It integrates traditional knowledge with modern science to create resilient food systems. In Western countries, the objectives of ecological farming are gaining traction as climate change, soil degradation, and food safety concerns push farmers and policymakers toward sustainable solutions. With 30% of global soils degraded (FAO, 2021, source), it offers a way to restore ecosystems while feeding growing populations.
Core Objectives of Ecological Farming
Ecological farming pursues interconnected goals to transform agriculture into a sustainable, resilient system. Below are its five core objectives, each vital to addressing modern environmental and social challenges.
1. Restore and Maintain Soil Health
Soil is the foundation of agriculture, and ecological farming prioritizes its long-term health through practices like composting, cover cropping, and fostering microbial diversity. For instance, compost adds organic matter, improving soil structure, while cover crops like clover prevent erosion and fix nitrogen. These objectives of ecological farming for soil restoration counteract the 24 billion tons of topsoil lost annually to erosion (UNCCD, 2017, source). By enhancing soil fertility naturally, farmers reduce dependency on synthetic fertilizers, ensuring productivity for future generations.
2. Enhance Biodiversity in Agricultural Systems
It promotes biodiversity by creating habitats for wildlife and diversifying crops. Hedgerows, wildflower strips, and polycultures support pollinators and natural pest predators, reducing the need for chemical interventions. The farm biodiversity objectives of ecological farming are critical, as 75% of global food crops rely on pollinators (IPBES, 2016, source). By fostering diverse ecosystems, farmers create resilient farms that thrive amid environmental changes.
3. Reduce External Chemical Inputs
Reducing synthetic pesticides and fertilizers is a cornerstone of ecological farming. Farmers use biopesticides, such as neem oil, and local seed varieties adapted to regional conditions to minimize environmental harm. The objective to reduce synthetic input in ecological agriculture addresses the 4.1 million tons of pesticides applied globally each year (FAO, 2020, source). This approach protects water sources and human health while maintaining crop yields.
4. Promote Climate Resilience
It’s builds resilience against climate challenges like droughts and floods. Drought-tolerant crops, such as millet, and water-saving techniques, like drip irrigation, help farms adapt. In the USA and UK, the ecological farming objectives for climate resilience align with goals to reduce agricultural greenhouse gas emissions, which account for 10% of total emissions in these regions (EPA, 2023, source). These practices ensure food security in a warming world.
5. Ensure Economic Viability for Farmers
It’s supports farmers’ livelihoods through diversified income streams, such as agro-tourism or direct-to-consumer sales, and lower input costs. By reducing reliance on expensive chemicals, farmers can achieve sustainable profit objectives in ecological farming. In the EU, agroecological farms report 20% higher profitability than conventional farms due to premium markets (EIP-AGRI, 2022, source).
Fundamental Principles of Ecological Farming
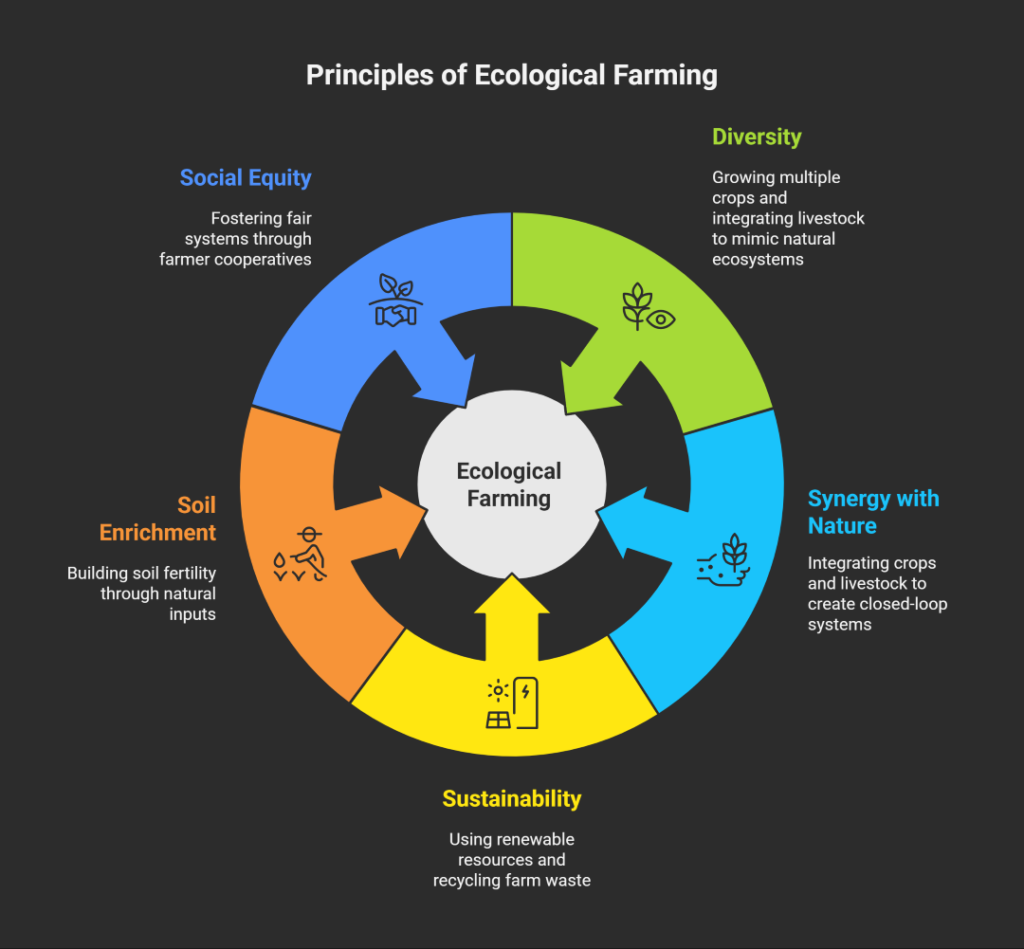
1. Principle of Diversity
Diversity is central to ecological farming. Farmers grow multiple crops and integrate livestock to mimic natural ecosystems. This agroecology principle of biodiversity reduces risks from pests and market fluctuations. For example, a UK farm might combine wheat, legumes, and pasture for livestock, enhancing resilience.
2. Principle of Synergy with Nature
Ecological farming works with natural cycles, integrating crops and livestock to create closed-loop systems. For instance, manure from livestock fertilizes fields, reducing external inputs. This ecological farming synergy with natural cycles ensures farms function as self-sustaining ecosystems.
3. Principle of Sustainability & Resource Efficiency
Using renewable resources like solar energy and recycling farm waste, ecological farming minimizes environmental impact. The resource-efficient ecological agriculture principles help farmers cut costs and reduce emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
4. Principle of Soil Enrichment
Building soil fertility through natural inputs like compost and green manure is key. These principles of ecological farming for soil health restore degraded soils, with studies showing a 25% increase in soil organic matter after five years of ecological practices (Rodale Institute, 2020, source).
5. Principle of Social & Economic Equity
Ecological farming fosters fair systems through farmer cooperatives and equitable pricing. The agroecological farming social sustainability principle ensures farmers and communities thrive, as seen in EU cooperatives that boost farmer incomes by 15% (EC, 2021, source).
Practices That Reflect Ecological Farming Principles
Principles come to life through practical applications, with real-world examples across the USA, UK, and EU.
- Crop Rotation and Polycultures: Rotating crops like corn and beans in the USA enhances soil fertility and disrupts pest cycles.
- Cover Cropping and Mulching: UK farmers use clover cover crops to prevent soil erosion, with 60% of agroecological farms adopting this practice (Soil Association, 2023, source).
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): In the EU, IPM reduces pesticide use by 50% through natural predators (EFSA, 2022, source).
- Agroforestry Systems: Combining trees with crops, as seen in French vineyards, boosts biodiversity and sequesters carbon.
- Organic Compost and Green Manure: US farms like Polyface Farm use compost to cut fertilizer costs by 30% (Polyface Farm, 2023, source).
Key Benefits of Ecological Farming in the Western World
Ecological farming delivers measurable benefits, particularly in Western countries facing environmental and economic pressures. Below is a summary table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Regeneration | Increases organic matter and microbial richness, improving fertility. |
| Climate Change Mitigation | Sequesters carbon and reduces emissions through low-input practices. |
| Biodiversity Protection | Supports pollinators and beneficial insects, enhancing ecosystem resilience. |
| Economic Security for Farmers | Reduces input costs and taps into premium markets for sustainable products. |
| Safer Food Systems | Eliminates toxic residues, building consumer trust in food safety. |
These benefits of ecological farming in Western countries address critical issues like the 14% decline in pollinator populations in North America (USDA, 2023, source). Moreover, ecological farming’s low-emission practices make it better for the environment, reducing agriculture’s carbon footprint by up to 20% (IPCC, 2022, source).
How Ecological Farming Differs from Organic Farming
While ecological and organic farming share goals, their approaches differ. The table below compares them with conventional farming:
| Aspect | Ecological Farming | Organic Farming | Conventional Farming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inputs | Minimal, natural (e.g., biopesticides) | Organic-certified, no synthetics | Heavy synthetic fertilizers/pesticides |
| Biodiversity | High, integrated ecosystems | Moderate, crop-focused | Low, monoculture-based |
| Certification | Often uncertified, principle-based | Strict certification (USDA, EU) | No sustainability certification |
| Scale | Small to medium, community-focused | Small to large, market-driven | Large-scale, industrial |
In the EU and North America, organic farming’s certification requirements can exclude small farmers, while ecological farming’s flexibility makes it accessible. The ecological farming vs organic farming difference lies in its holistic focus on local ecosystems and social equity, not just chemical avoidance.
Future of Ecological Farming in the West
The future of agroecological farming in the USA, UK, and Europe is promising, driven by policy and consumer trends. The EU’s Green Deal aims for 25% of farmland to be organic or agroecological by 2030 (EC, 2020, source). The USDA’s Climate-Smart Agriculture program incentivizes ecological practices with $3 billion in funding (USDA, 2023, source). Consumers increasingly demand sustainable food, with 70% of UK shoppers prioritizing eco-friendly products (YouGov, 2023, source). Challenges include scaling practices and educating farmers, but opportunities like premium markets and carbon credits offer growth potential.
Final Thoughts – Why Ecological Farming Is the Future of Sustainable Agriculture
Ecological farming’s objectives, restoring soil, enhancing biodiversity, reducing chemicals, building climate resilience, and ensuring economic viability—align with the urgent needs of Western agriculture. Its principles of diversity, synergy, sustainability, soil enrichment, and equity provide a roadmap for resilient food systems. To support this movement, adopt ecological products, advocate for sustainable policies, or explore our Sustainable Agriculture blog. Together, we can build a future where farming nourishes both people and the planet.